Original Author – Your name will be added here if you created the original content for this page.
Main Contributors – Danielle Anderson, Administration, Beth Thorpe, Judy Muftí, kim jackson and WikiSysop
Description
Features of the motion detection input device that may provide benefits in physical therapy:
- Includes an RGB video camera and a depth-sensing camera. The depth camera has two components, an infrared laser that projects a point cloud and an infrared camera that records the point projection pattern.
- Interprets 3D scene information from continuous data collection. This requires precise positioning and movement for the subject to successfully perform a movement.
- Provides very precise measurement of joint positioning, including range of motion, twist, and angular velocity.
- Hands-free games allow specific functional training for tasks with increasing difficulty levels, enabling a variety of personalized exercise programs.
- Provides immediate feedback to both the physical therapist and the patient, which can help develop correct movement patterns.
Precision in Clinical Practice
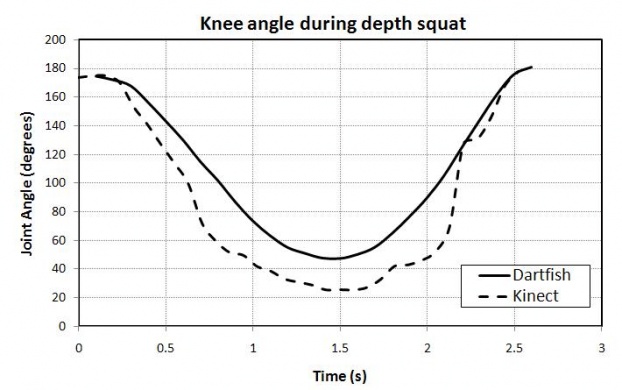
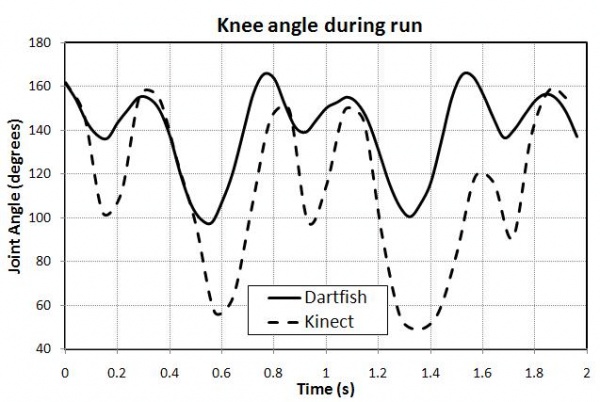
From the following blog article comparing running motion analysis between Dartfish and Kinect:
Kinect is not as precise as Dartfish. However, it is much more affordable and does not require the patient to wear special clothing.
Real-time human pose recognition in parts from single depth images. Shotton et al., 2011
Shotton et al. proposed and tested a new method to rapidly and accurately predict 3D body joint positions from a single depth image using a pixel-wise classification system. The system operates at 200 frames per second, allowing real-time interaction. Kinect was able to identify joints regardless of body position with 98.4% accuracy using over 1,000,000 real images. Kinect can detect depth of 1 cm and length and width of 3 mm.
Since June 2010, Kinect has been commercially available as a complementary tool for the X-Box system. There are many fitness, sports, and other games that can assist physical therapy clients in performing functional movements, cardiovascular exercises, and therapeutic exercises. Furthermore, because these games are engaging and entertaining, clients are likely to have higher motivation to complete their therapeutic exercises daily. Patients could receive a download token for their Xbox, and the custom therapy game would help patients to do exercises on days between actual physical therapy visits.
In July 2011, Microsoft Research released Kinect Beta SDK for Windows. This non-commercial software development tool allows software engineers to develop programs that act as an interface between Windows and Kinect. The potential of this tool in physical therapy is greatly enhanced by the ability to use Kinect with a PC. For example, therapists could use this tool to create individualized home exercise programs that the patient could follow at home. Data would be recorded about the quality and quantity of each exercise performed so that the therapist could review the patient’s progress.
The following video shows the result of a program designed with Kinect Beta SDK for Windows.
The points shown are three-dimensional representations of joints. The program continuously displays the angle of each joint in relation to two neighboring joints as the subject moves in front of the Kinect.
Microsoft Kinect
Advantages in Physical Therapy
- Economical tool: sold for $149.00 (USD)
- Can download the free beta version of Kinect software for Windows to create programs for use on a PC (http://research.microsoft.com/en-us/um/redmond/projects/kinectsdk/download.aspx)
- Provides instant feedback to both patients and therapists.
- Does not require the use of any body-attached or handheld device (i.e., motion sensors, handheld remotes, standing on an object, etc.)
- Difficult to «cheat» during activities due to camera’s ability to detect and track full body position.
- Can increase motivation levels to complete exercise programs at home as they can be seen as a fun activity (Chang 2011)
- Can be used for upper extremity gross motor exercises for wheelchair-bound individuals (Chang 2011)
Disadvantages in physical therapy
- Software is still in development.
- Precision is questionable (refer to the precision section above)
- More research is needed to harness the full potential of Kinect regarding biomechanics.
- Not all patients will have or be able to afford to buy a Kinect
- Therapists will need training to learn how to use Kinect (specifically how to develop a home exercise program for a patient through Kinect).
- Not all clinics will have a Kinect available for use (clinics will need to purchase one)
- Not capable of detecting fine motor movements.
Resources
References
Shotton J, Fitzgibbon A, Cook M, Blake A et al. Real-time human pose recognition in parts from single depth images. CVPR. 2011.
Chang Y, Chen S, Huang J. Kinect-based system for physical rehabilitation: a pilot study for young adults with motor disabilities. Res Dev Disable. 2011; 32: 2566-2570